A Soundscape is the sonic experience of being in a space. It contains sonic events that take place in a space and duration. We hear significant sounds (that clearly tell us where we are) and the space (the reverberation or ambience), some in foreground and some in background.
The World Soundscape Project was a research and educational endeavor founded in 1969 by Canadian composer R. Murray Schafer at Simon Fraser University (SFU). The project established the modern field of study known as acoustic ecology or soundscape studies, which is concerned with raising public awareness of sound, documenting environmental sound and its changing character, and establishing the concept and practice of soundscape design as an alternative to noise pollution. Read more here
Space
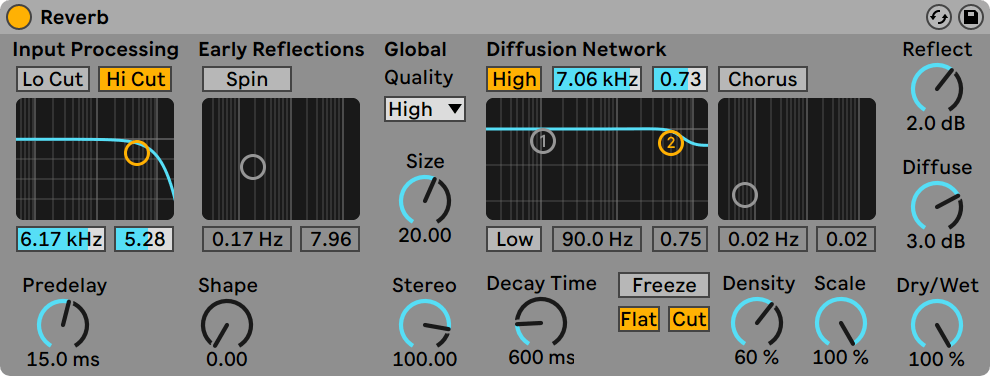
Reverb (all versions)
Predelay controls the delay time, in milliseconds, before the onset of the first early reflection. This delays the reverberation relative to the input signal. One’s impression of the size of a real room depends partly on this delay. Typical values for ”natural” sounds range from 1ms to 25ms.
Early Reflection are the earliest echoes that you hear after they bounce off a room’s walls, before the onset of the diffused reverberation ”tail.” Their amplitude and distribution give an impression of the room’s character.
The Shape control ”sculpts” the prominence of the early reflections, as well as their overlap with the diffused sound.
Rhythm
Delay (all versions) and Echo (all versions)
Grain Delay (Intro, Standard and Suite only)
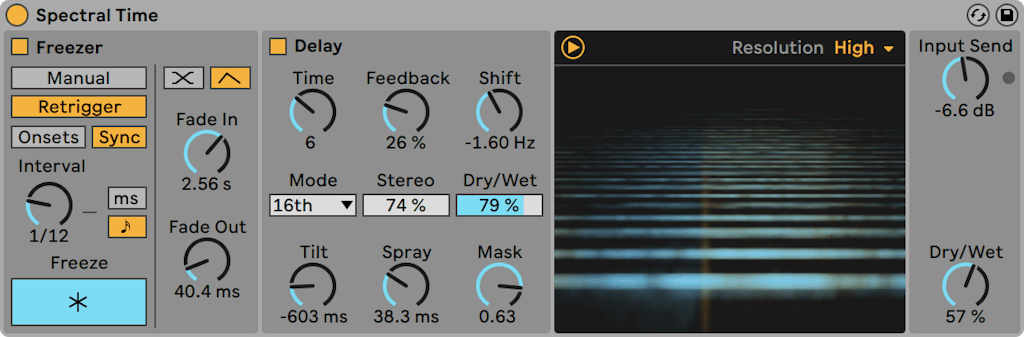
Spectral Time (Live Suite only)
- In Manual mode, audio can be frozen by clicking on the Freeze button. You can also control the Fade In and Fade Out time of the frozen signal in milliseconds.
- In Retrigger mode, you have more controls to fine-tune the rhythm of the frozen audio, which can be frozen automatically at every transient (onset), or at regular intervals.
- Onsets mode will freeze the audio after a transient is detected in the input. Use the Sensitivity knob to adjust the sensitivity of onset detection. Sensitivity is highest at 100% and lowest at 0%.
- Sync mode will freeze the audio at regular intervals, determined by the Interval control. By toggling the Freezer Time Unit buttons, the Interval control can be set to either milliseconds or beat-time values.
- The Time parameter controls the delay time for the spectral delay lines. The type of value shown here is dependent on the unit type chosen in the “Mode” drop-down chooser:
- Shift shifts the frequency of the delayed signals. Each successive delay will be shifted up or down by the specified frequency amount.
- Stereo adjusts the width of the Tilt and Spray controls.
Melody
Simpler (all versions)
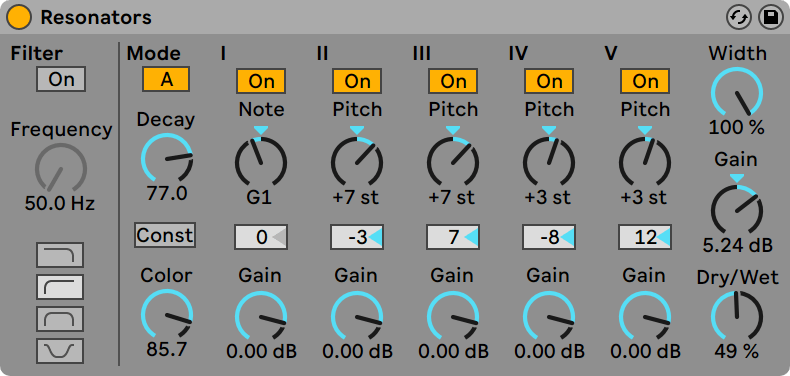
Resonators (Live Standard and Suite only)
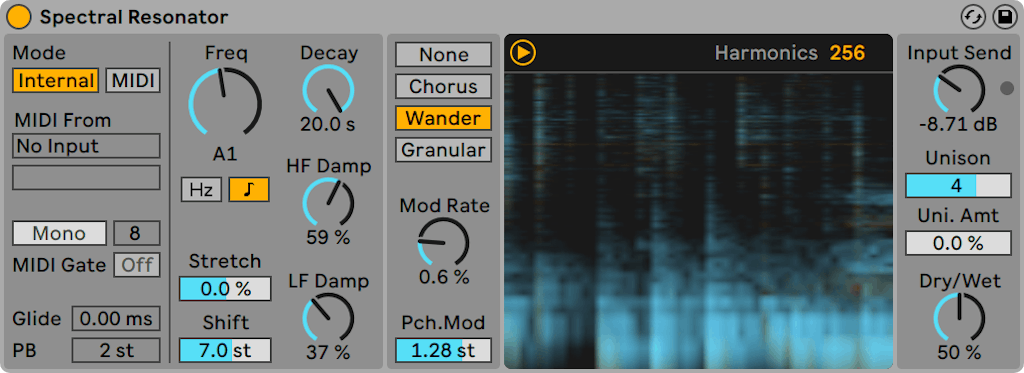
Spectral Resonator (Live Suite only)
- None applies no modulation.
- Chorus applies triangle wave modulation for every partial. When Mod Rate is set to 0, this mode only modulates the amplitudes of the partials.
- Wander uses random sawtooth waveforms as the modulation source for each partial.
- Granular modulates the amplitude of all partials randomly, using exponential decay envelopes. The partials are generated at random and, in this mode, the Mod Rate parameter affects the density of the partials.

Comments